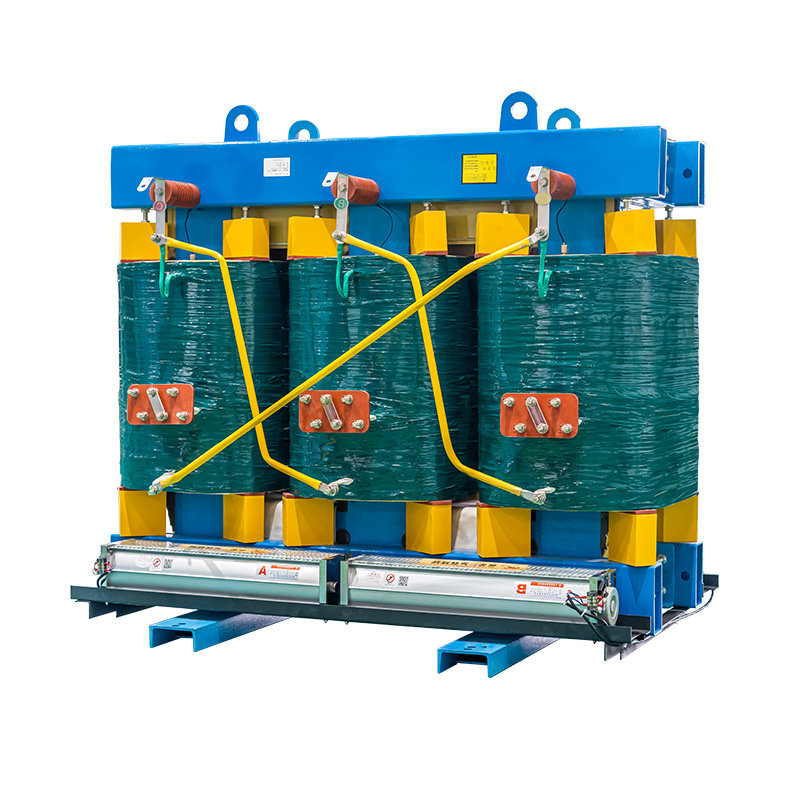
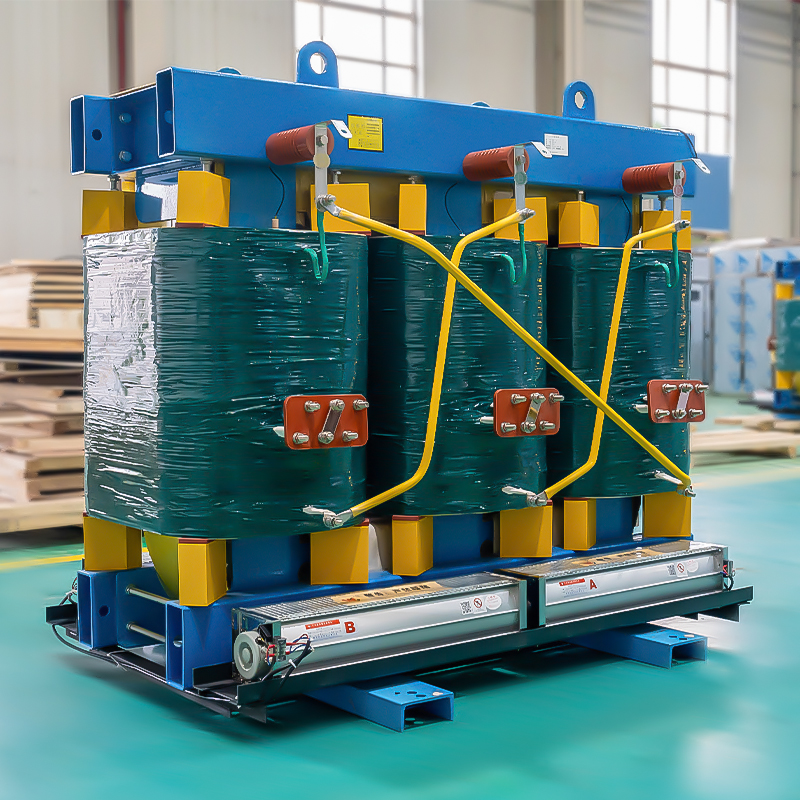
Amorphous alloy transformers, developed in the 1970s, are a new type of electrical transformer that utilizes amorphous alloy instead of silicon steel as the core material. They exhibit a significant reduction in no-load losses, around 70%-80% lower than silicon steel core transformers, and a drop of approximately 85% in no-load current. These transformers are currently among the most energy-efficient distribution transformers available. They are suitable for applications where distribution efficiency is low, and there are stringent requirements for fire resistance, such as rural electrical grids, high-rise buildings, commercial centers, subways, airports, stations, industrial and mining enterprises, and power plants.
Compared to conventional transformers, a 2500kVA amorphous alloy transformer can save 21,000 kWh of electricity annually. Taking 50 units as an example, this translates to an annual electricity savings of 1.05 million kWh and a reduction in coal consumption by 420 tons. Additionally, it contributes to a reduction in carbon dioxide emissions by approximately 1,050 tons.
Design and performance characteristics:
1. Design
Adopt advanced electromagnetic design optimization software to improve the accuracy and speed of amorphous alloy dry-type transformer design, and realize design automation and optimization. Powerful simulation analysis capabilities, for each series of products, through simulation analysis of flow field, temperature field, leakage magnetic field, short-circuit force, etc., to ensure product safety and reliability.
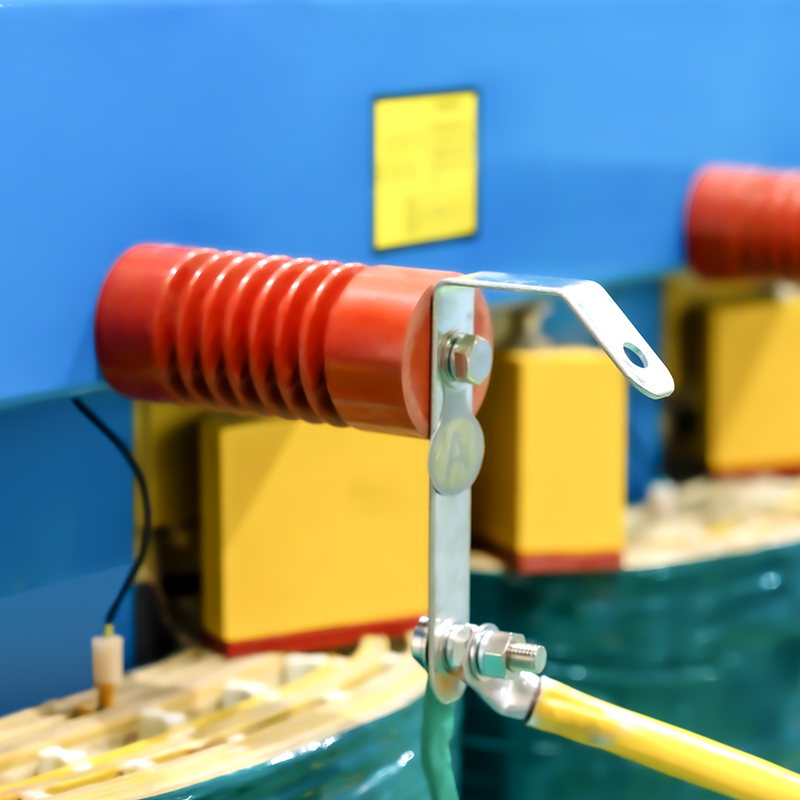
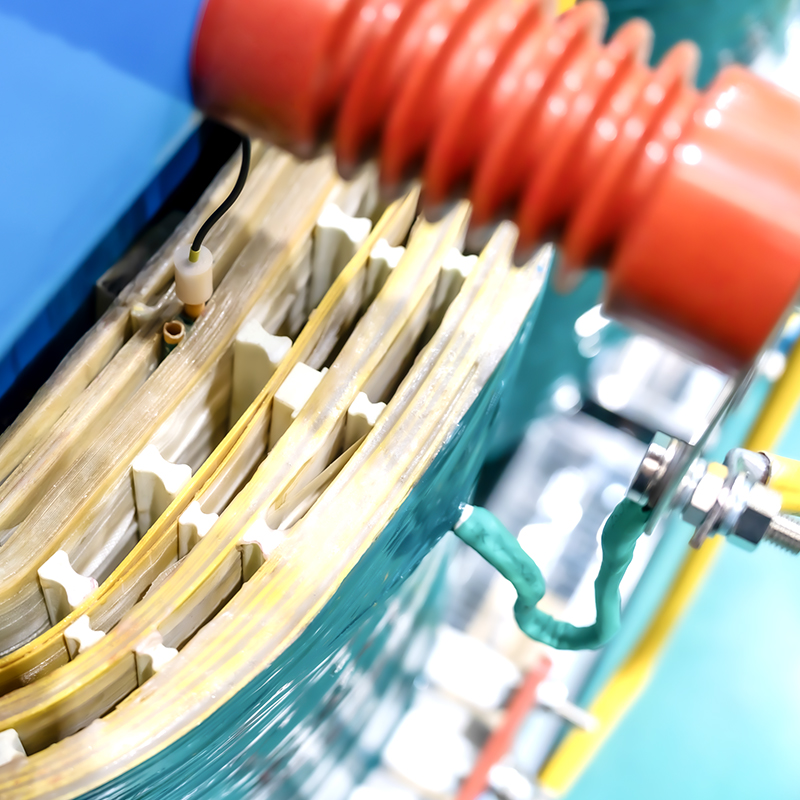
2. Iron core
Using high-quality amorphous strip materials to create Three-Phase Three-Limb cores, subjected to annealing under the influence of a direct current magnetic field to achieve outstanding characteristics of low iron loss and low excitation current. The core surface is coated with a special resin to prevent moisture and corrosion. The core structure is simple, with high mechanical strength, resistance to high-order harmonics, and 70% to 80% lower iron loss compared to conventional products.
3. Low voltage foil winding coils
Employ imported high-quality copper foil and H-class insulation materials wound on molded insulation cylinders. Layer insulation is made of NOMEX paper, and VPI vacuum pressure impregnation solidifies it into a sturdy whole. The upper and lower ends are sealed with resin. The copper bars and foils are welded using specialized equipment. These coils exhibit high mechanical strength, strong short-circuit resistance, and excellent resistance to dust, moisture, and salt spray.
4. High voltage winding coils
Using a multi-layer segmented cylindrical design with a longitudinal multi-channel structure. They exhibit strong resistance to heat and shock, as well as excellent impulse withstand capability. The conductor is composed of NOMEX paper-wrapped flat copper wire, with NOMEX paper used for layer insulation and H-class material for end insulation. After VPI vacuum pressure impregnation, the coils undergo high-temperature baking for curing. The upper and lower ends are sealed with resin, ensuring good heat dissipation and preventing cracking.
5. Assembly
Utilize the coil as the load-bearing main body, which is supported on a separate winding system and fixed by compression. The iron core employs a suspended structure so that the iron core is not under pressure, which reduces the influence of radial shrinkage and expansion on the iron core when the transformer is short-circuited. The overlapping part of the iron core adopts a special glue end-sealing process to ensure the minimum force on the iron core.


 Tiếng Việt
Tiếng Việt